update
This commit is contained in:
@@ -62,3 +62,84 @@ For matching:
|
|||||||
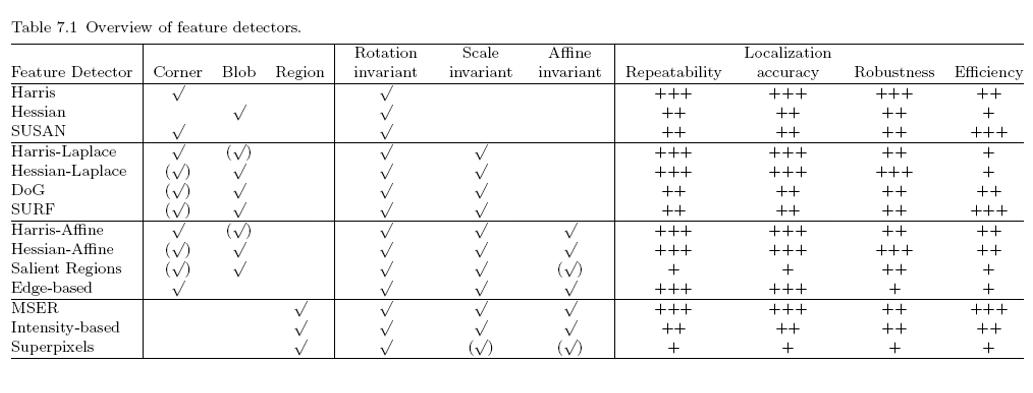
## Local feature matching
|
## Local feature matching
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Matching
|
### Matching
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Simplest approach: Pick the nearest neighbor. Threshold on absolute distance
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Problem: Lots of self similarity in many photos
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Solution: Nearest neighbor with low ratio test
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
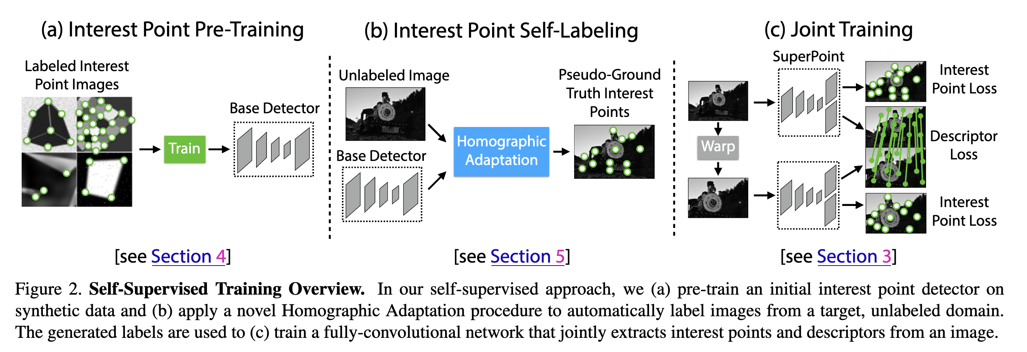
## Deep Learning for Correspondence Estimation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Optical Flow
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Field
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Motion field: the projection of the 3D scene motion into the image
|
||||||
|
Magnitude of vectors is determined by metric motion
|
||||||
|
Only caused by motion
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Optical flow: the apparent motion of brightness patterns in the image
|
||||||
|
Magnitude of vectors is measured in pixels
|
||||||
|
Can be caused by lightning
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Brightness constancy constraint, aperture problem
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Machine Learning Approach
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- Collect examples of inputs and outputs
|
||||||
|
- Design a prediction model suitable for the task
|
||||||
|
- Invariances, Equivariances; Complexity; Input and Output shapes and semantics
|
||||||
|
- Specify loss functions and train model
|
||||||
|
- Limitations: Requires training the model; Requires a sufficiently complete training dataset; Must re-learn known facts; Higher computational complexity
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Optimization Approach
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- Define properties we expect to hold for a correct solution
|
||||||
|
- Translate properties into a cost function
|
||||||
|
- Derive an algorithm to solve for the cost function
|
||||||
|
- Limitations: Often requires making overly simple assumptions on properties; Some tasks can’t be easily defined
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Given frames at times $t-1$ and $t$, estimate the apparent motion field $u(x,y)$ and $v(x,y)$ between them
|
||||||
|
Brightness constancy constraint: projection of the same point looks the same in every frame
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
I(x,y,t-1) = I(x+u(x,y),y+v(x,y),t)
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Additional assumptions:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- Small motion: points do not move very far
|
||||||
|
- Spatial coherence: points move like their neighbors
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Trick for solving:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Brightness constancy constraint:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
I(x,y,t-1) = I(x+u(x,y),y+v(x,y),t)
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Linearize the right-hand side using Taylor expansion:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
I(x,y,t-1) \approx I(x,y,t) + I_x u(x,y) + I_y v(x,y)
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
I_x u(x,y) + I_y v(x,y) + I(x,y,t) - I(x,y,t-1) = 0
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Hence,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
I_x u(x,y) + I_y v(x,y) + I_t = 0
|
||||||
|
$$
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
BIN
public/CSE559A/Comparison_of_keypoint_detectors.png
Normal file
BIN
public/CSE559A/Comparison_of_keypoint_detectors.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 105 KiB |
BIN
public/CSE559A/Deep_learning_for_correspondence_estimation.png
Normal file
BIN
public/CSE559A/Deep_learning_for_correspondence_estimation.png
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 232 KiB |
Reference in New Issue
Block a user