upgrade structures and migrate to nextra v4
This commit is contained in:
71
content/CSE559A/CSE559A_L19.md
Normal file
71
content/CSE559A/CSE559A_L19.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
# CSE559A Lecture 19
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Detection
|
||||
|
||||
### Behavior of corner features with respect to Image Transformations
|
||||
|
||||
To be useful for image matching, “the same” corner features need to show up despite geometric and photometric transformations
|
||||
|
||||
We need to analyze how the corner response function and the corner locations change in response to various transformations
|
||||
|
||||
#### Affine intensity change
|
||||
|
||||
Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
- Only derivative of intensity are used (invariant to intensity change)
|
||||
- Intensity scaling
|
||||
|
||||
#### Image translation
|
||||
|
||||
Solution:
|
||||
|
||||
- Derivatives and window function are shift invariant
|
||||
|
||||
#### Image rotation
|
||||
|
||||
Second moment ellipse rotates but its shape (i.e. eigenvalues) remains the same
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scaling
|
||||
|
||||
Classify edges instead of corners
|
||||
|
||||
## Automatic Scale selection for interest point detection
|
||||
|
||||
### Scale space
|
||||
|
||||
We want to extract keypoints with characteristic scales that are equivariant (or covariant) with respect to scaling of the image
|
||||
|
||||
Approach: compute a scale-invariant response function over neighborhoods centered at each location $(x,y)$ and a range of scales $\sigma$, find scale-space locations $(x,y,\sigma)$ where this function reaches a local maximum
|
||||
|
||||
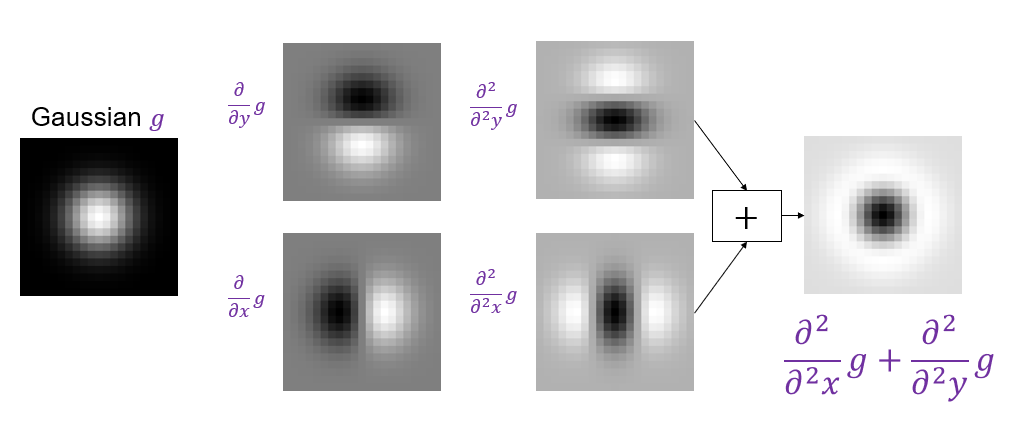
A particularly convenient response function is given by the scale-normalized Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter:
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\nabla^2_{norm}=\sigma^2\nabla^2\left(\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}g+\frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2}g\right)
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
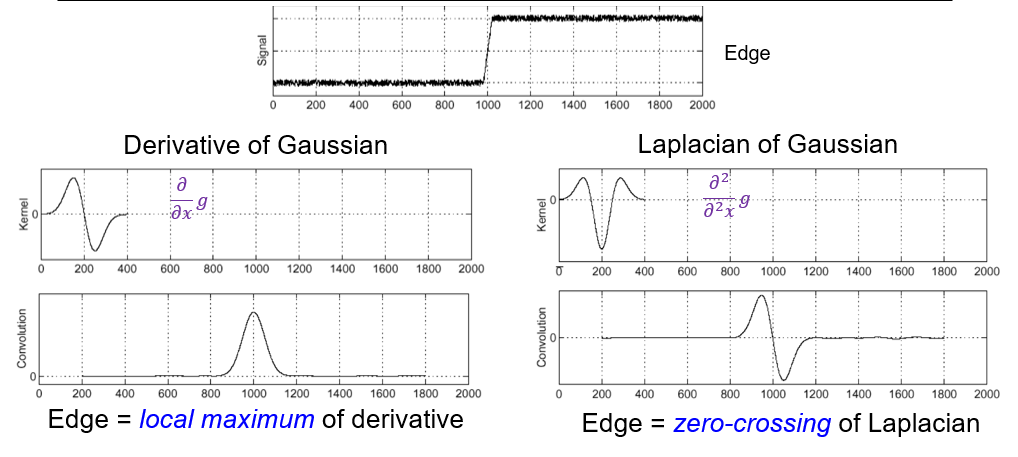
#### Edge detection with LoG
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
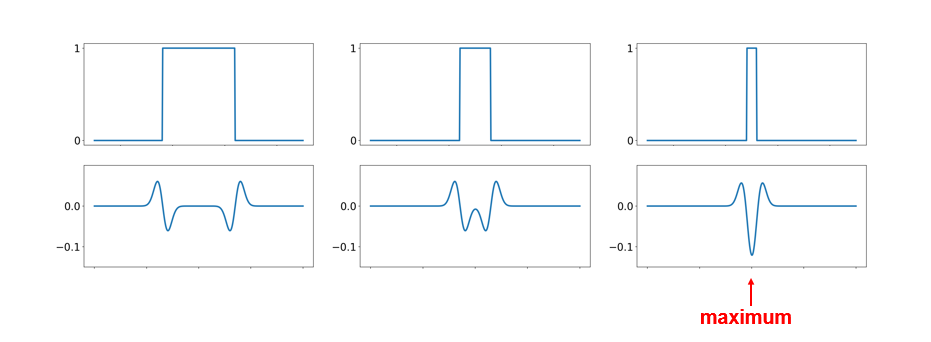
#### Blob detection with LoG
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Difference of Gaussians (DoG)
|
||||
|
||||
DoG has a little more flexibility, since you can select the scales of the Gaussians.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT)
|
||||
|
||||
The main goal of SIFT is to enable image matching in the presence of significant transformations
|
||||
|
||||
- To recognize the same keypoint in multiple images, we need to match appearance descriptors or "signatures" in their neighborhoods
|
||||
- Descriptors that are locally invariant w.r.t. scale and rotation can handle a wide range of global transformations
|
||||
|
||||
### Maximum stable extremal regions (MSER)
|
||||
|
||||
Based on Watershed segmentation algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
Select regions that are stable over a large parameter range
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user