upgrade structures and migrate to nextra v4
This commit is contained in:
102
content/CSE559A/CSE559A_L9.md
Normal file
102
content/CSE559A/CSE559A_L9.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
||||
# CSE559A Lecture 9
|
||||
|
||||
## Continue on ML for computer vision
|
||||
|
||||
### Backpropagation
|
||||
|
||||
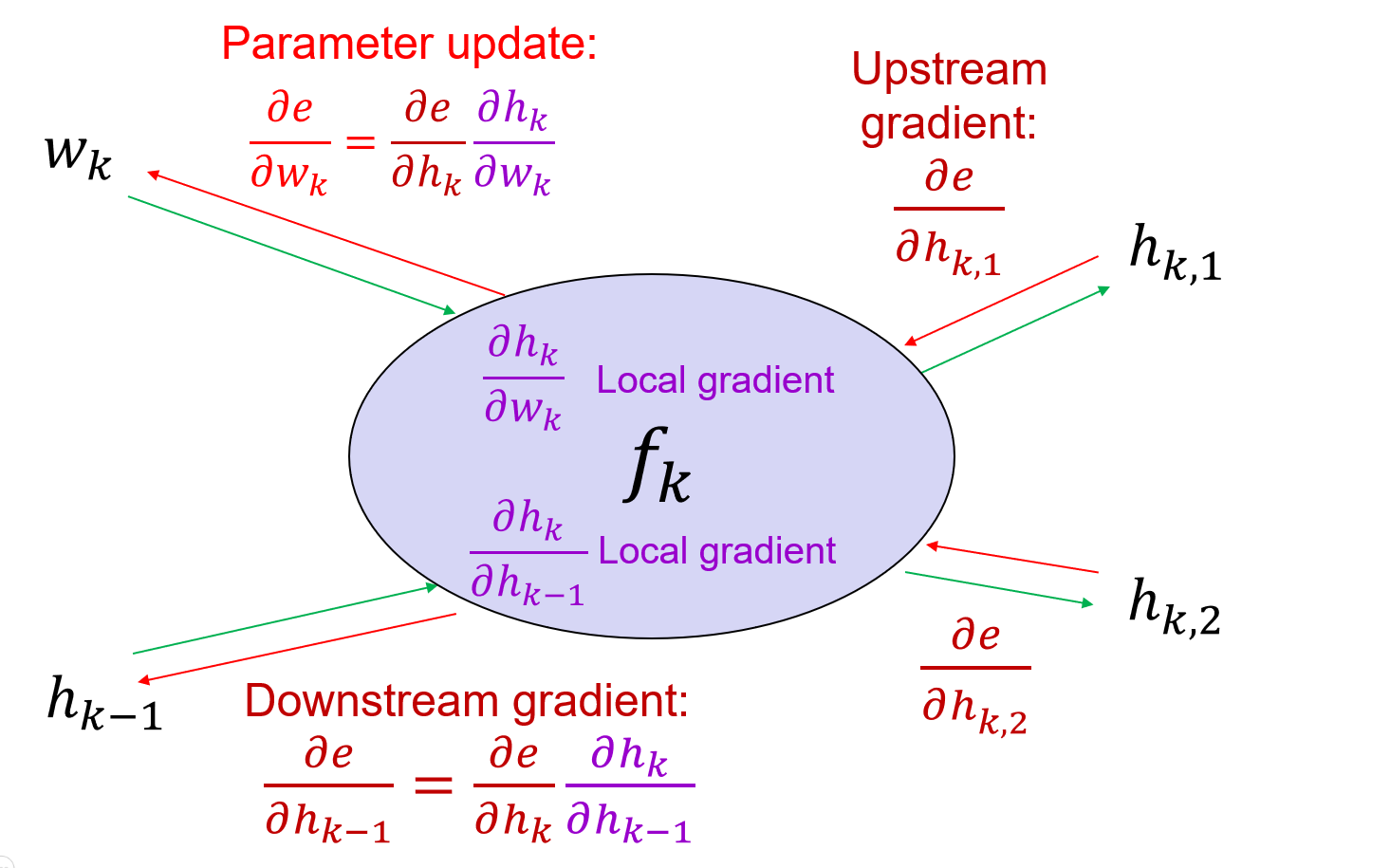
#### Computation graphs
|
||||
|
||||
SGD update for each parameter
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
w_k\gets w_k-\eta\frac{\partial e}{\partial w_k}
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
$e$ is the error function.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using the chain rule
|
||||
|
||||
Suppose $k=1$, $e=l(f_1(x,w_1),y)$
|
||||
|
||||
Example: $e=(f_1(x,w_1)-y)^2$
|
||||
|
||||
So $h_1=f_1(x,w_1)=w^T_1x$, $e=l(h_1,y)=(y-h_1)^2$
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\frac{\partial e}{\partial w_1}=\frac{\partial e}{\partial h_1}\frac{\partial h_1}{\partial w_1}
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\frac{\partial e}{\partial h_1}=2(h_1-y)
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\frac{\partial h_1}{\partial w_1}=x
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\frac{\partial e}{\partial w_1}=2(h_1-y)x
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
For the general cases,
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\frac{\partial e}{\partial w_k}=\frac{\partial e}{\partial h_K}\frac{\partial h_K}{\partial h_{K-1}}\cdots\frac{\partial h_{k+2}}{\partial h_{k+1}}\frac{\partial h_{k+1}}{\partial h_k}\frac{\partial h_k}{\partial w_k}
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
Where the upstream gradient $\frac{\partial e}{\partial h_K}$ is known, and the local gradient $\frac{\partial h_k}{\partial w_k}$ is known.
|
||||
|
||||
#### General backpropagation algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
The adding layer is the gradient distributor layer.
|
||||
The multiplying layer is the gradient switcher layer.
|
||||
The max operation is the gradient router layer.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Simple example: Element-wise operation (ReLU)
|
||||
|
||||
$f(x)=ReLU(x)=max(0,x)$
|
||||
|
||||
$$
|
||||
\frac{\partial z}{\partial x}=\begin{pmatrix}
|
||||
\frac{\partial z_1}{\partial x_1} & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\
|
||||
0 & \frac{\partial z_2}{\partial x_2} & \cdots & 0 \\
|
||||
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
|
||||
0 & 0 & \cdots & \frac{\partial z_n}{\partial x_n}
|
||||
\end{pmatrix}
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
Where $\frac{\partial z_i}{\partial x_j}=1$ if $i=j$ and $z_i>0$, otherwise $\frac{\partial z_i}{\partial x_j}=0$.
|
||||
|
||||
When $\forall x_i<0$ then $\frac{\partial z}{\partial x}=0$ (dead ReLU)
|
||||
|
||||
Other examples on ppt.
|
||||
|
||||
## Convolutional Neural Networks
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Convolutional layer
|
||||
|
||||
#### Flatten layer
|
||||
|
||||
Fully connected layer, operate on vectorized image.
|
||||
|
||||
With the multi-layer perceptron, the neural network trying to fit the templates.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Convolutional layer
|
||||
|
||||
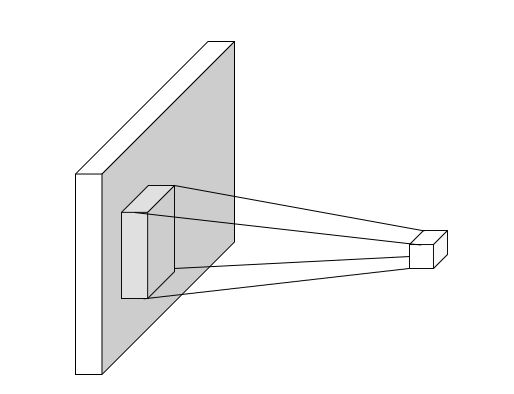
Limit the receptive fields of units, tiles them over the input image, and share the weights.
|
||||
|
||||
Equivalent to sliding the learned filter over the image , computing dot products at each location.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Padding: Add a border of zeros around the image. (higher padding, larger output size)
|
||||
|
||||
Stride: The step size of the filter. (higher stride, smaller output size)
|
||||
|
||||
### Variants 1x1 convolutions, depthwise convolutions
|
||||
|
||||
### Backward pass
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user