Some checks failed
Sync from Gitea (main→main, keep workflow) / mirror (push) Has been cancelled
132 lines
3.1 KiB
Markdown
132 lines
3.1 KiB
Markdown
# CSE4303 Introduction to Computer Security (Lecture 3)
|
||
|
||
## Network attacks
|
||
|
||
### Internet Infrastructures
|
||
|
||
Local and interdomain routing
|
||
|
||
- TCP/IP for routing and messaging
|
||
- BGP for routing announcements
|
||
|
||
Domain Name System
|
||
|
||
- Find IP address from symbolic name (cse.wustl.edu)
|
||
|
||
Media Access Control (MAC) addresses in the network access layer
|
||
|
||
- Associated w/ network interface card (NIC)
|
||
- 00-50-56-C0-00-01
|
||
|
||
IP addresses for the network layer
|
||
|
||
- IPv4(32 bit) vs IPv6(128 bit)
|
||
- 128.1.1.3 vs fe80::fc38:6673:f04d:b37b%4
|
||
|
||
IP addresses + ports for the transport layer
|
||
|
||
- E.g., 10.0.0.2:8080
|
||
|
||
Domain names for the application/human layer
|
||
|
||
- E.g., www.wustl.edu
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
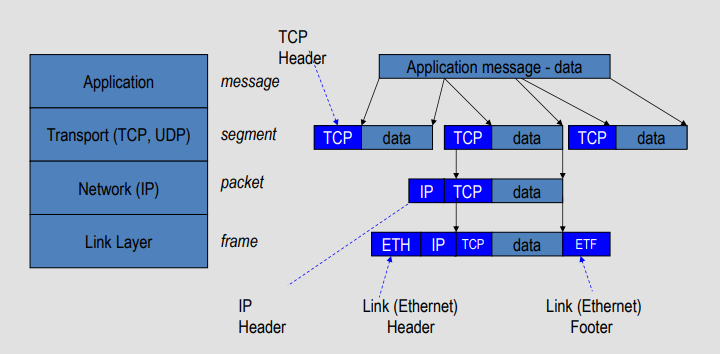
|
||
|
||
### Wireshark
|
||
|
||
Wireshark is a packet sniffer and protocol analyzer
|
||
|
||
- Captures and analyzes frames
|
||
- Supports plugins
|
||
|
||
Usually required to run with administrator privileges
|
||
|
||
Setting the network interface in promiscuous mode captures traffic across the entire LAN segment and not just frames addressed to the machine
|
||
|
||
### Examining the link layer
|
||
|
||
When a packet arrives at the destination subnet, MAC address is used to deliver the packet
|
||
|
||
#### ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
|
||
|
||
- Each IP node (Host, Router) on LAN has ARP table
|
||
- ARP Table: IP/MAC address mappings for some LAN nodes
|
||
`< IP address; MAC address; TTL>`
|
||
- TTL (Time To Live): time after which address mapping will be forgotten (typically 20 min)
|
||
|
||
#### Lack of Source Authentication - ARP Spoofing (ARP Poisoning)
|
||
|
||
Send fake or 'spoofed', ARP messages to an Ethernet LAN.
|
||
|
||
- To have other machines associate IP addresses with the attacker’s MAC
|
||
|
||
Legitimate use
|
||
|
||
- Implementing redundancy and fault tolerance
|
||
|
||
#### ARP Poisoning (Spoofing) Defense
|
||
|
||
Prevention
|
||
|
||
- Static ARP table
|
||
- DHCP Certification (use access control to ensure that hosts only use the IP addresses assigned to them, and that only authorized DHCP servers are accessible).
|
||
|
||
Detection
|
||
|
||
- Arpwatch (sending email when updates occur)
|
||
|
||
### Examining the network layer
|
||
|
||
Internet Protocol (IP)
|
||
|
||
Connectionless
|
||
|
||
- Unreliable
|
||
- Best effort
|
||
|
||
Notes:
|
||
|
||
- src and dest ports not parts of IP hdr
|
||
|
||
#### IP Protocol Functions (Summary)
|
||
|
||
Routing
|
||
|
||
- IP host knows location of router (gateway)
|
||
- IP gateway must know route to other networks
|
||
|
||
Fragmentation and reassembly
|
||
|
||
- If max-packet-size less than the user-data-size
|
||
|
||
Error reporting
|
||
|
||
- ICMP packet to source if packet is dropped
|
||
|
||
TTL field: decremented after every hop
|
||
|
||
- Packet dropped if TTL=0. Prevents infinite loops
|
||
|
||
#### Problem: no src IP authentication
|
||
|
||
Client is trusted to embed correct source IP
|
||
|
||
- Easy to override using raw sockets
|
||
|
||
- Libnet: a library for formatting raw packets with arbitrary IP headers
|
||
|
||
- Scapy: a python library for packet crafting
|
||
|
||
Anyone who owns their machine can send packets with arbitrary source IP
|
||
|
||
- ... response will be sent back to forged source IP
|
||
|
||
Implications:
|
||
|
||
- Anonymous DoS attacks;
|
||
- Anonymous infection attacks (e.g. slammer worm)
|
||
|