4.4 KiB
CSE559A Lecture 26
Continue on Geometry and Multiple Views
The Essential and Fundamental Matrices
Math of the epipolar constraint: Calibrated case
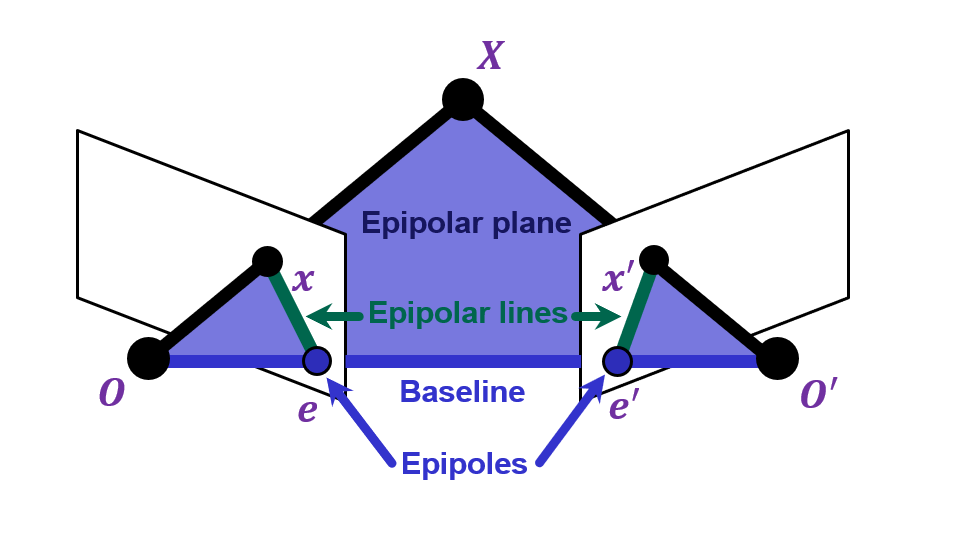
Recall Epipolar Geometry
Epipolar constraint:
If we set the config for the first camera as the world origin and [I|0]\begin{pmatrix}y\\1\end{pmatrix}=x, and [R|t]\begin{pmatrix}y\\1\end{pmatrix}=x', then
Notice that x'\cdot [t\times (Ry)]=0
x'^\top E x_1 = 0
We denote the constraint defined by the Essential Matrix as E.
E x is the epipolar line associated with x (l'=Ex)
E^\top x' is the epipolar line associated with x' (l=E^\top x')
E e=0 and E^\top e'=0 (x and x' don't matter)
E is singular (rank 2) and have five degrees of freedom.
Epipolar constraint: Uncalibrated case
If the calibration matrices K and K' are unknown, we can write the epipolar constraint in terms of unknown normalized coordinates:
x'^\top_{norm} E x_{norm} = 0
where x_{norm}=K^{-1} x, x'_{norm}=K'^{-1} x'
x'^\top_{norm} E x_{norm} = 0\implies x'^\top_{norm} Fx=0
where F=K'^{-1}EK^{-1} is the Fundamental Matrix.
(x',y',1)\begin{bmatrix}
f_{11} & f_{12} & f_{13} \\
f_{21} & f_{22} & f_{23} \\
f_{31} & f_{32} & f_{33}
\end{bmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}
x\\y\\1
\end{pmatrix}=0
Properties of F:
F x is the epipolar line associated with x (l'=F x)
F^\top x' is the epipolar line associated with x' (l=F^\top x')
F e=0 and F^\top e'=0
F is singular (rank two) and has seven degrees of freedom
Estimating the fundamental matrix
Given: correspondences x=(x,y,1)^\top and x'=(x',y',1)^\top
Constraint: x'^\top F x=0
(x',y',1)\begin{bmatrix}
f_{11} & f_{12} & f_{13} \\
f_{21} & f_{22} & f_{23} \\
f_{31} & f_{32} & f_{33}
\end{bmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}
x\\y\\1
\end{pmatrix}=0
Each pair of correspondences gives one equation (one constraint)
At least 8 pairs of correspondences are needed to solve for the 9 elements of F (The eight point algorithm)
We know F needs to be singular/rank 2. How do we force it to be singular?
Solution: take SVD of the initial estimate and throw out the smallest singular value
F=U\begin{bmatrix}
\sigma_1 & 0 \\
0 & \sigma_2 \\
0 & 0
\end{bmatrix}V^\top
Structure from Motion
Not always uniquely solvable.
If we scale the entire scene by some factor k and, at the same time, scale the camera matrices by the factor of 1/k, the projections of the scene points remain exactly the same:
x\cong PX =(1/k P)(kX)
Without a reference measurement, it is impossible to recover the absolute scale of the scene!
In general, if we transform the scene using a transformation Q and apply the inverse transformation to the camera matrices, then the image observations do not change:
x\cong PX =(P Q^{-1})(QX)
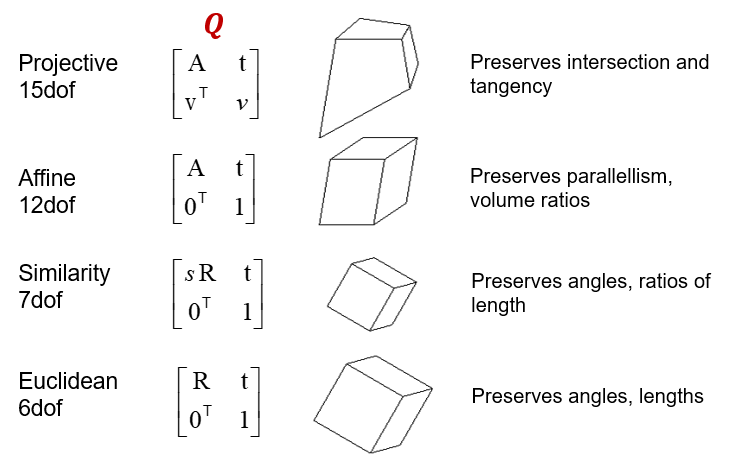
Types of Ambiguities
Affine projection : more general than orthographic
A general affine projection is a 3D-to-2D linear mapping plus translation:
P=\begin{bmatrix}
a_{11} & a_{12} & a_{13} & t_1 \\
a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{23} & t_2 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}
A & t \\
0^\top & 1
\end{bmatrix}
In non-homogeneous coordinates:
\begin{pmatrix}
x\\y\\1
\end{pmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}
a_{11} & a_{12} & a_{13} \\
a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{23}
\end{bmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}
X\\Y\\Z
\end{pmatrix}+\begin{pmatrix}
t_1\\t_2
\end{pmatrix}=AX+t
Affine Structure from Motion
Given: 𝑚 images of 𝑛 fixed 3D points such that
x_{ij}=A_iX_j+t_i, \quad i=1,\dots,m, \quad j=1,\dots,n
Problem: use the 𝑚𝑛 correspondences x_{ij} to estimate 𝑚 projection matrices A_i and translation vectors t_i, and 𝑛 points X_j
The reconstruction is defined up to an arbitrary affine transformation Q (12 degrees of freedom):
\begin{bmatrix}
A & t \\
0^\top & 1
\end{bmatrix}\rightarrow\begin{bmatrix}
A & t \\
0^\top & 1
\end{bmatrix}Q^{-1}, \quad \begin{pmatrix}X_j\\1\end{pmatrix}\rightarrow Q\begin{pmatrix}X_j\\1\end{pmatrix}
How many constraints and unknowns for m images and n points?
2mn constraints and 8m + 3n unknowns
To be able to solve this problem, we must have 2mn \geq 8m+3n-12 (affine ambiguity takes away 12 dof)
E.g., for two views, we need four point correspondences